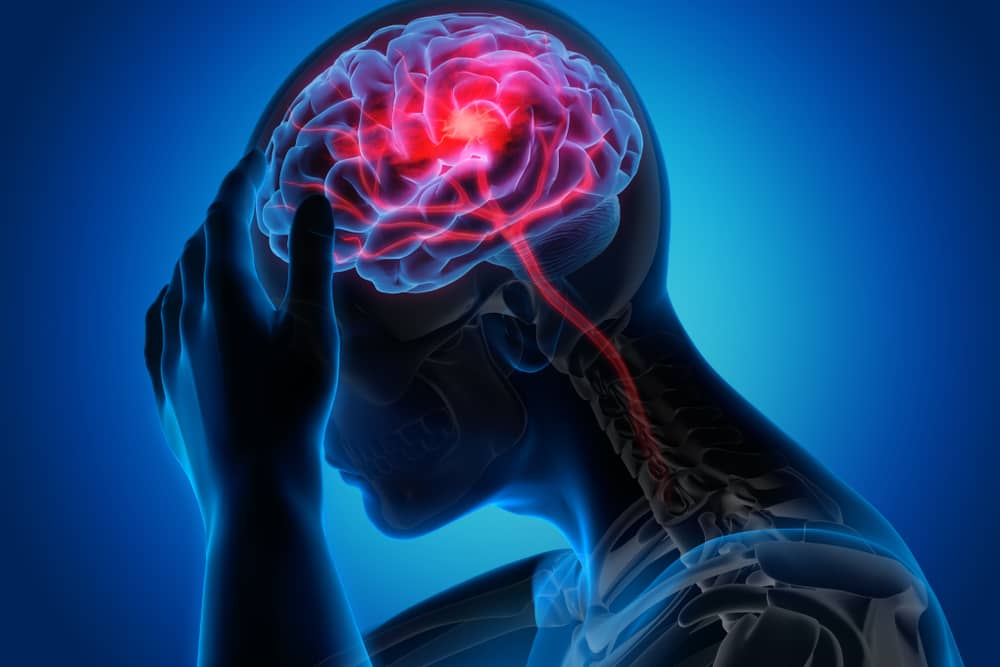
All You Need to Know About Brain Hemorrhage Recovery Time, Causes, and Symptoms
When a patient experiences a brain hemorrhage, they will begin to feel dizziness and headache. Sometimes their vision can get worse. A neurological examination will show symptoms of Brain Hemorrhage such as swelling in the brain and bleeding, but many people will experience pain. At this time, doctors are not sure what caused the bleeding or if a tumor has been sent into the brain. For these reasons, brain hemorrhaging recovery time is often difficult to predict. However, the prognosis is good for most of those who recover from brain hemorrhage.
The sooner you start recovering after experiencing a brain hemorrhage, the better your odds of survival and long-term quality of life. Your doctor may recommend testing of blood and other markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and troponin T in order to rule out tumors, which should reduce the risk of an early death.
Tests Should Be Performed Shortly After the Injury
Brain hemorrhage recovery time varies from 24 hours to several days after the first sign of severe head trauma. It also seems that brain injury can occur at any moment. Some injuries may show no signs or just the slightest symptoms. This includes car accidents, sports injuries, falls, motor vehicle incidents, and even suicide. Injuries may affect one side of the brain or both sides, with some injuries resulting in permanent brain damage.
As a result of traumatic brain injury, it is critical that injured patients have a well-trained medical team who knows how to care for them in a coordinated effort. Fortunately, this level of training is available through specialized centers such as University Health Network’s Traumatic Brain Injury Center where trained professionals work with patients.
Contact the Specialists
Patients are taught how to walk by themselves once every three months, which helps them learn how to use tools they already know. Even now, some years after the initial injury, most individuals do not regain full function of their brains. Fortunately, there is continued research about brain repair and rehabilitation, and most experts agree that it is possible to reverse the effects of brain injury by learning new skills and using them in different ways.
Brain hemorrhage recovery time depends on multiple factors, each of which have its own unique role to play. These include the nature of the injury itself, symptoms caused by it, and the person’s response to the injury, as well as their overall health and fitness. Each of these factors contributes to a faster post-injury return to pre-injury activities and also can affect survival. People who fall well below the injury threshold experience shorter times to come back to pre-injury activities than individuals whose injuries were more severe.
They are more likely to suffer another brain injury that requires additional treatment. In addition to pre-injury activity, recovery is affected by the strength of the brain tissue to heal once back at full strength. Poor nutrition and poor fluid intake are common contributing factors. Individuals who struggle with alcohol abuse, depression, and other mental health conditions have difficulty rehabilitating after brain hemorrhage, requiring longer hospital stays and increased expenses.
Possible Recovery Time
Those with a past history of drug abuse or alcohol abuse have the highest risk as they cannot afford rehab in the first place. There are two general treatments for brain hemorrhage. Surgery is one of the most effective therapies and is considered by most specialists to be a “first-line” measure for brain hemorrhages because it preserves the brain’s brain matter. While surgery is very successful, it is expensive and is associated with complications ranging from infections to breathing problems that hinder an individual’s ability to breathe properly, including for prolonged periods of time.
Medication is usually an option, but doctors often prescribe benzodiazepines (such as Valium and Xanax) due to excessive sedation used to allow surgeons to perform the surgical procedure. Other therapies which can help an individual adapt to life with a brain hemorrhage include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and pharmacotherapy. Both are non-invasive treatments, but CBT teaches patients how to manage emotions and cope with life while receiving psychosocial support in a group setting.
Pharmacotherapy Can Improve Memory Problems
Patients typically receive chemotherapy, radiation treatment, and immunotherapy, as well as targeted and muscle-controlling drugs. Although medical treatment is often the best course of action, the most common complication in brain hemorrhage rehab is pneumonia. This type of infection occurs when bacteria enter the lungs and then reach the bloodstream, where they cause septic shock, organ failure, and/or brain swelling.
Pneumonia may leave a person hospitalized and can require significant rehabilitation to return to daily personal and job responsibilities. Most importantly, though, pneumonia presents with no lasting symptoms and can be treated quickly if caught early.
There is a wide range of information available to inform and assist those who experience severe brain fractures. Many resources provide online resource guides, as well as webinars, videos, and other helpful materials to guide patients safely and effectively.
Also Read: Best Health Tips